1. Introduction & Motivation


Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models allow robots to interpret natural language commands. However, state-of-the-art models like OpenVLA require expensive hardware (Cloud GPUs, >24GB VRAM).
Our objective is educational: to create an accessible, low-cost platform for experimenting with VLAs. We pivoted to SmolVLA (~450M parameters) to run on consumer-grade hardware. We demonstrate that compact VLA architectures can generalize across robotic embodiments—specifically adapting the model to the WLKATA Mirobot (a 6-axis arm) without retraining from scratch.
2. Methodology & Hardware Stack
Hardware Setup
- Robot: WLKATA Mirobot 6-DOF arm.
- Compute: Local Inference on NVIDIA RTX 3050 (4GB VRAM) and Training on RTX 2080 Ti.
- Vision: A DIY wrist-mounted webcam (640x480) and a top-view Intel RealSense camera.
- Gripper: A custom DIY servo gripper & a stock servo gripper
Software Integration
We successfully registered the unsupported WLKATA Mirobot into the LeRobot framework by creating a custom Python environment. This unlocked built-in tools for teleoperation and dataset recording.
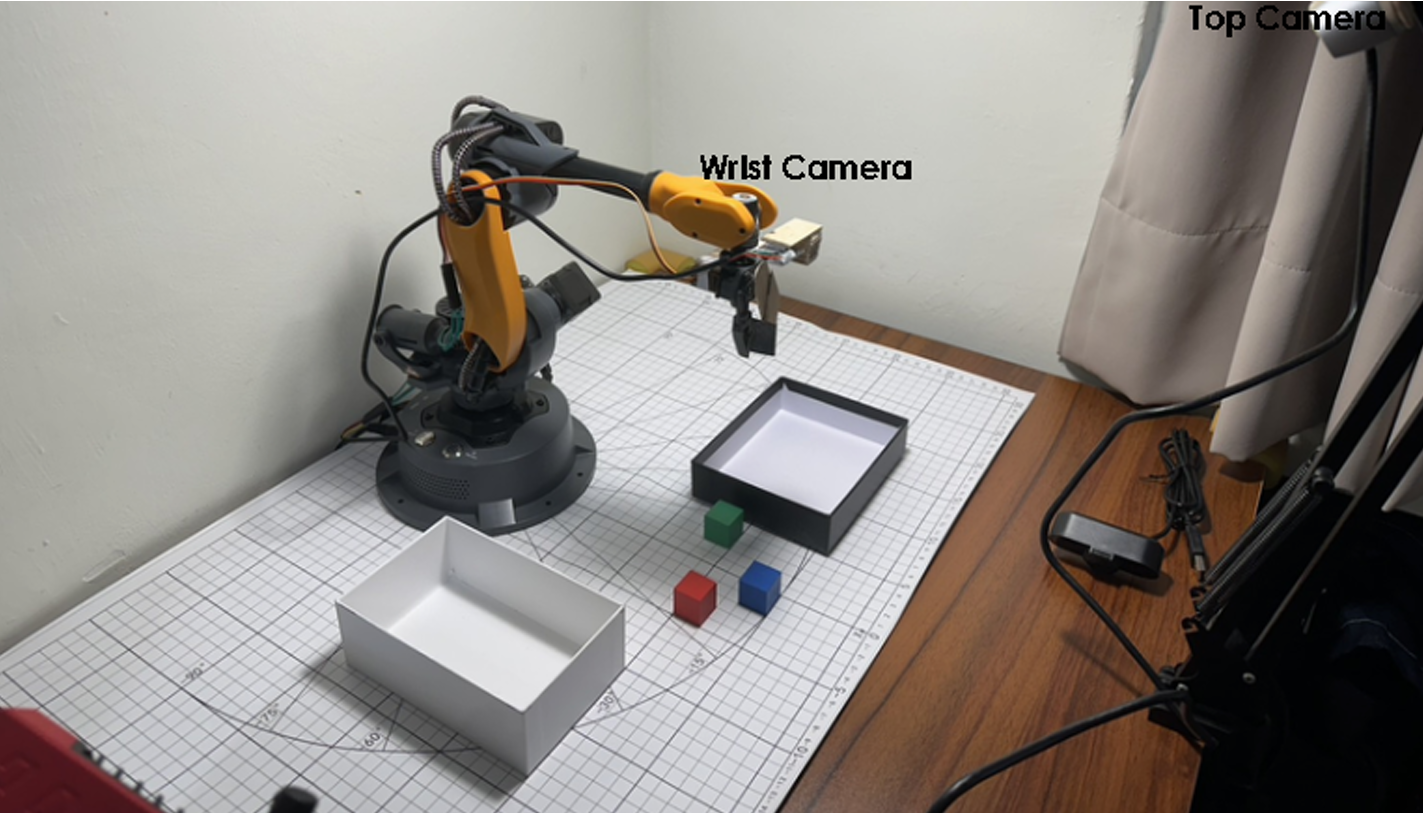
Figure: The "Home Setup" with wrist and top cameras.
3. Kinematic Safety Layer
Raw VLA models are unaware of physical constraints and can command actions that damage the robot. We implemented a two-stage safety layer between the model and the SDK:
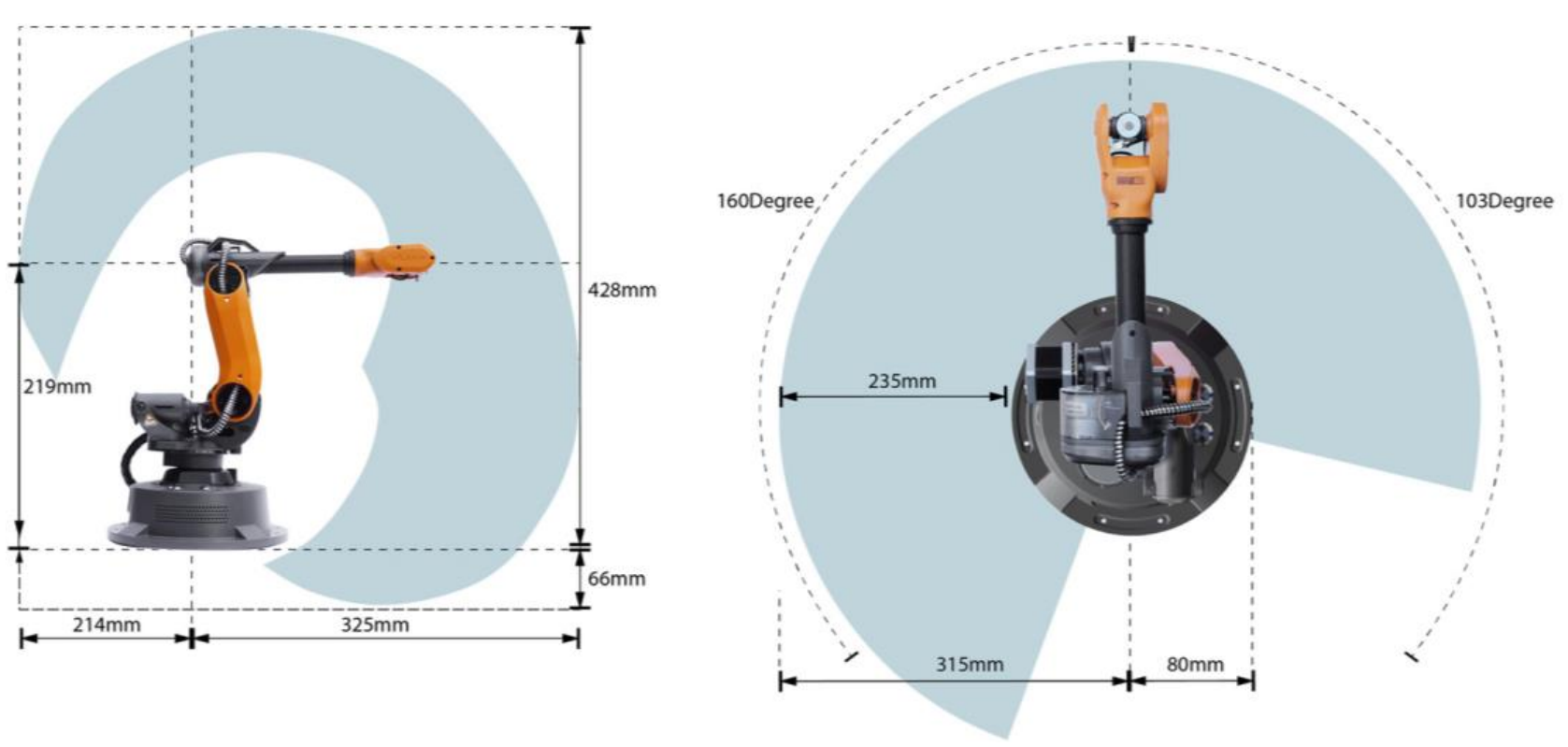
Figure: Mirobot workspace limits.
- End-Effector Pose Limiter: A "Box and Ring" clamp that enforces minimum and maximum horizontal reach to prevent the arm from hitting its base.
- Joint-Space Limiter (IK/FK): We use Inverse Kinematics (IK) to convert commanded Cartesian coordinates into joint angles. We then clip these angles to physical hardware limits (e.g., -110° to 160°) before converting them back via Forward Kinematics.
4. Results & Discussion
Cost-Benefit Analysis
SmolVLA makes VLA research financially viable for students:
| Metric | OpenVLA (SOTA) | SmolVLA (Ours) |
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | ~7 Billion | ~450 Million |
| VRAM Required | > 24 GB | 6 - 8 GB |
| Running Cost | ~$0.46 / hr (Cloud GPU) | $0.00 (Local Consumer PC) |
Task Performance
We evaluated the system on three tasks: Pick & Place, Sorting, and Stacking.
| Task | Trials | Success Rate | Avg. Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pick & Place (Initial) | 20 | 80% | 138s |
| Pick & Place (Final) | 20 | 30% | 132s |
| Stack Cubes | 20 | 10% | 146s |
Analysis: The "DIY Domain Shift"
Our initial tests showed high promise (80% success). However, performance dropped significantly in later trials. We identified the root cause as mechanical instability. The robot's "homing" sequence caused the bulky DIY wrist camera to slightly collide with the frame, altering the camera angle before every run. Since VLA models are highly sensitive to visual perspective, these micro-shifts caused inference failures.
5. Conclusion
This project provides a validated blueprint for adapting low-cost robots to modern VLA frameworks. We proved that the barrier to entry is not the model itself, but the consistency of the hardware setup.
- Success: Integrated WLKATA Mirobot into LeRobot and achieved language-conditioned control.
- Constraint: Quantified the "DIY Domain Shift," showing that camera stability is critical for lightweight VLA models.
- Future Work: We are upgrading to a rigid custom camera bracket to solve the homing collision issue.