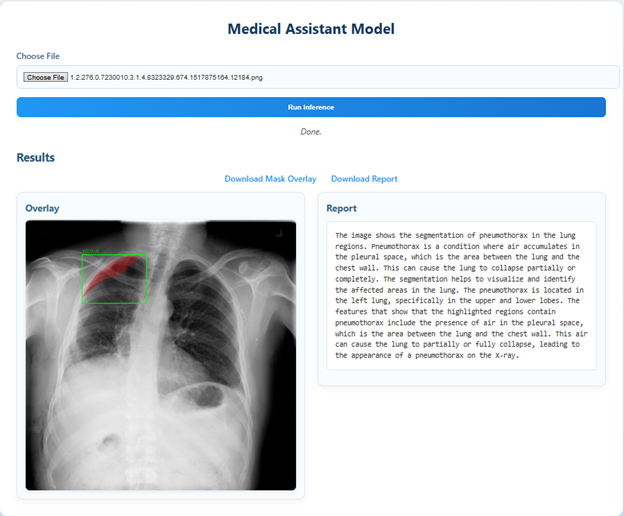
System Architecture
Our system uses a three-stage modular pipeline that combines computer vision and natural language processing:
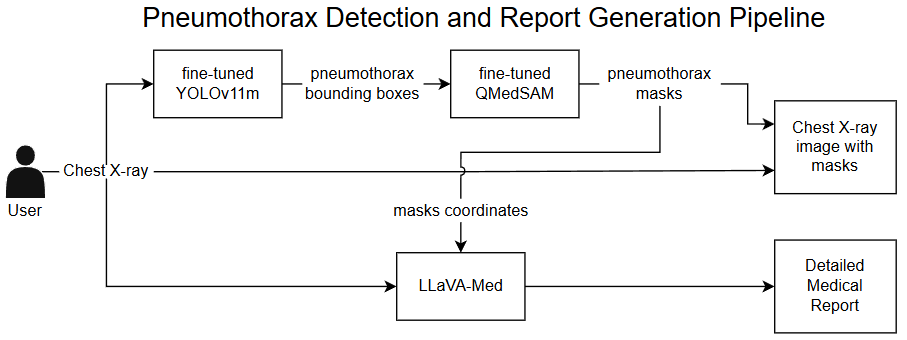
Figure 1. End-to-end pipeline integrating detection, segmentation, and report generation.
Detection
YOLOv11m
Identifies pneumothorax regions and generates bounding boxes
Segmentation
QMedSAM
Creates precise lesion masks from detected regions
Report Generation
LLaVA-Med
Generates comprehensive medical reports with visual context
YOLO Detection
Fine-tuned YOLOv11m on 12,047 chest X-rays for real-time pneumothorax localization. Achieves mAP@0.5 of 0.399 with robust performance on subtle lesions.
QMedSAM Segmentation
Quantized medical segmentation model trained with knowledge distillation. 75% smaller than MedSAM while maintaining 49% IoU accuracy.
LLaVA-Med Reporting
Medical-adapted vision-language model generating clinically relevant reports. Integrates mask coordinates for enhanced spatial awareness.