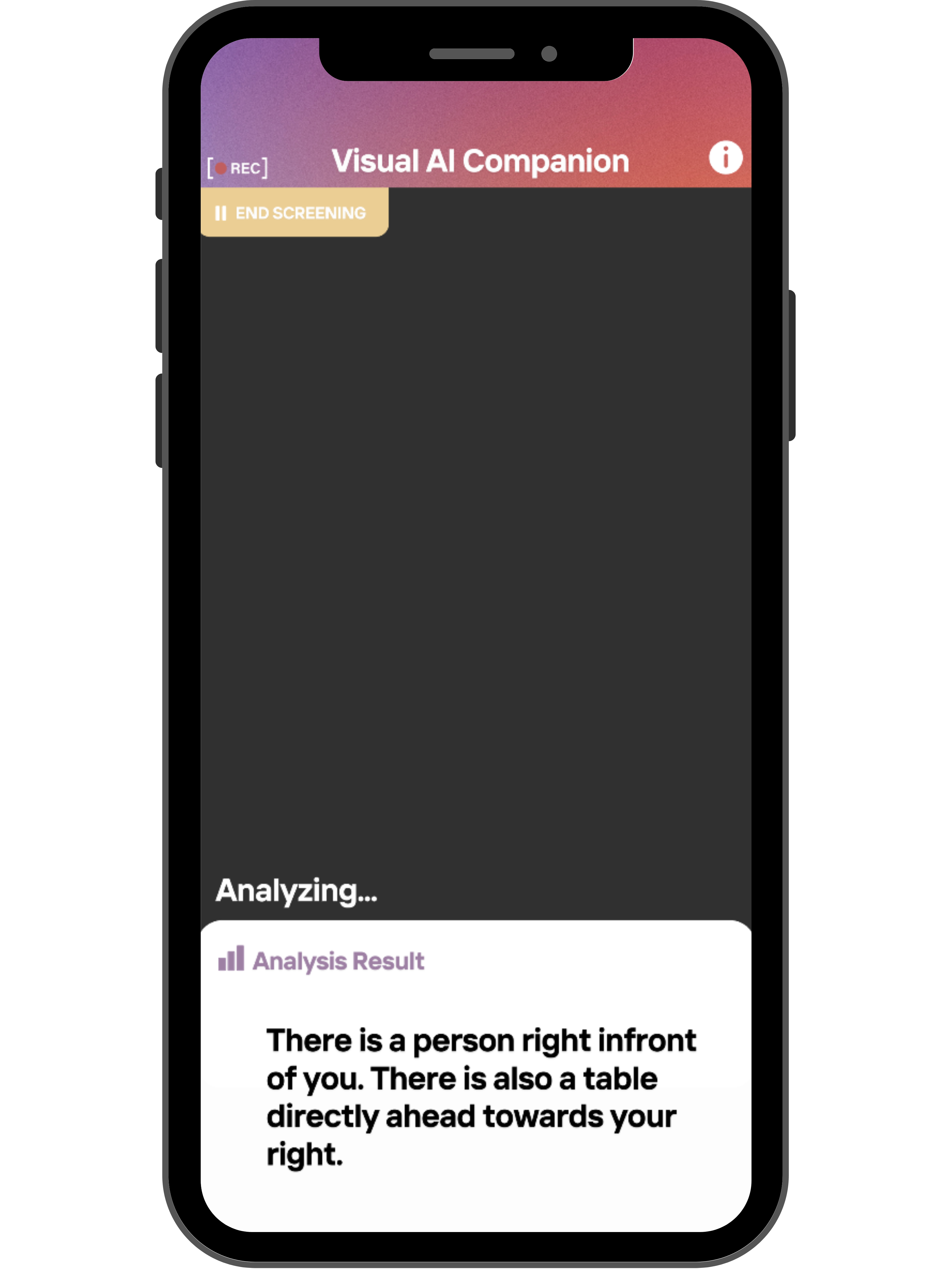
Visual AI Companion
A Real-Time Scene and Navigation Assistant for the Visually Impaired
國立清華大學資訊工程學系

國立清華大學資訊工程學系
Navigating everyday environments poses persistent challenges for visually impaired individuals, often limiting their independence and mobility. This research introduces the Visual AI Companion, a real-time scene and navigation assistant that leverages advanced AI technologies to enhance spatial awareness and safety.
Leveraging computer vision techniques including object recognition, obstacle detection, and depth estimation, the system provides guidance through its implementation on mobile applications. By translating visual data into actionable feedback, it empowers users to move through complex settings. Thus, the project aims to provide self-reliance and improve quality of life by offering an accessible tool tailored to the mobility needs of the visually impaired.
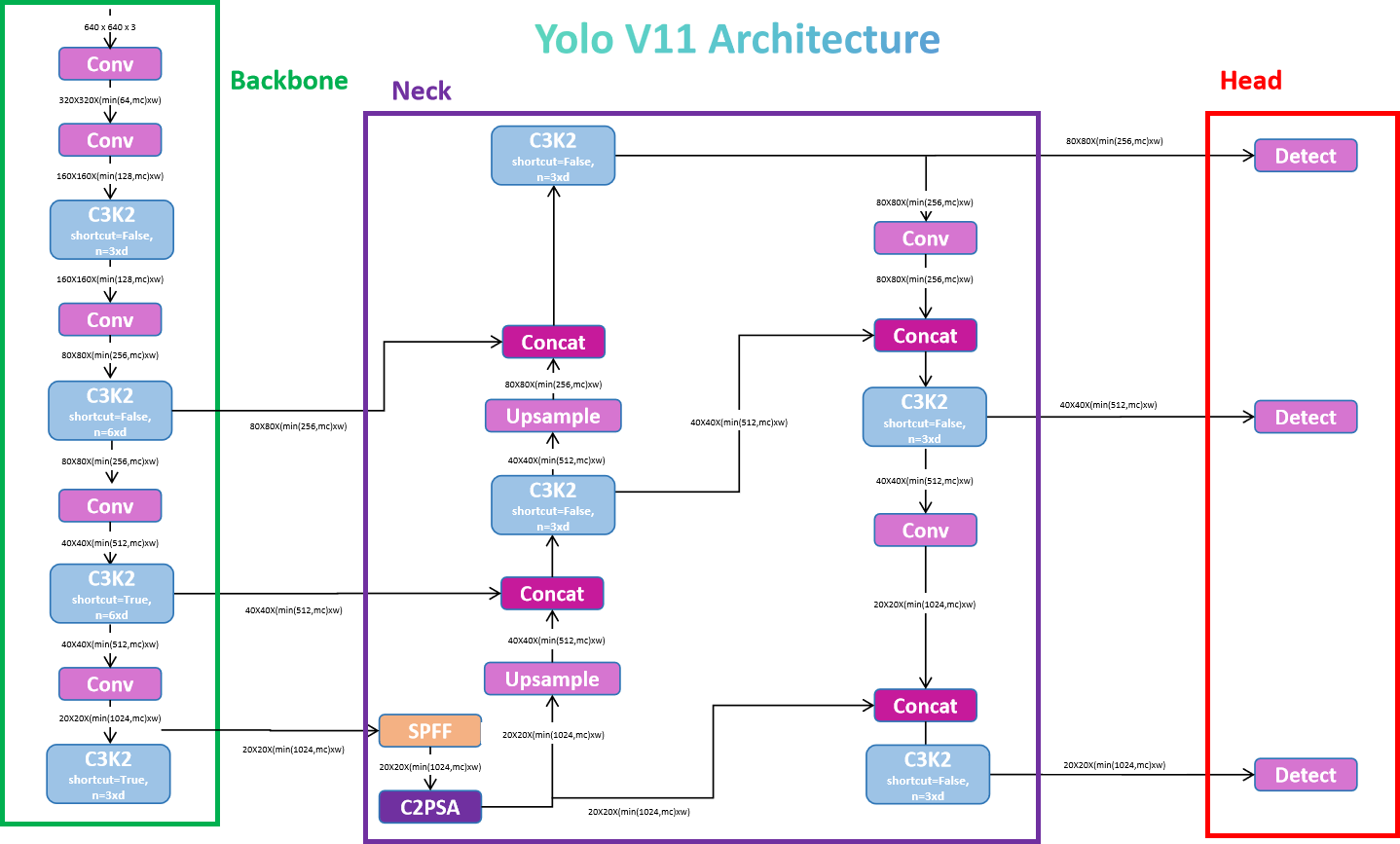
A real-time object detection model that identifies objects within a scene using bounding boxes and class labels. It enables the system to recognize common objects, people, vehicles, furniture, and electronics to better assist the user in understanding their environment.
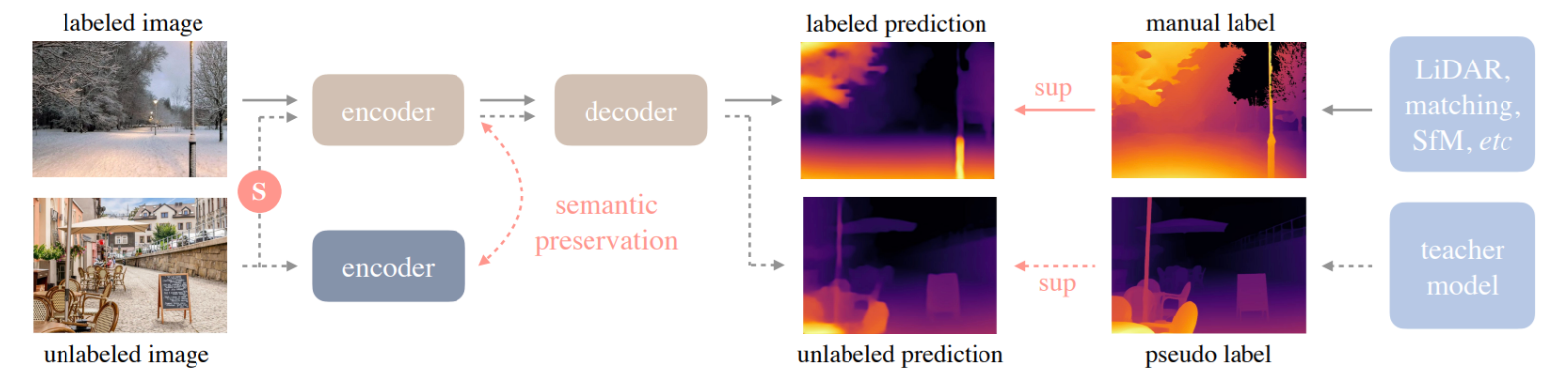
A monocular depth estimation model that predicts the relative distance of objects and surfaces from a single image. This allows the system to interpret spatial geometry and assess how far obstacles are from the user.
A text-to-speech engine integrated into the Flutter framework to provide real-time audio feedback to users. It enables hands-free navigation by converting visual information into spoken warnings and guidance, making the app truly accessible.
The system builds on the standard YOLOv11 model trained on the COCO dataset, which includes 80 object classes across categories like people, vehicles, furniture, and electronics. To better suit the context, we've curated a specialized dataset formatted accordingly. These additions enhance the system's ability to detect mobility-related hazards and provide more relevant object class information.
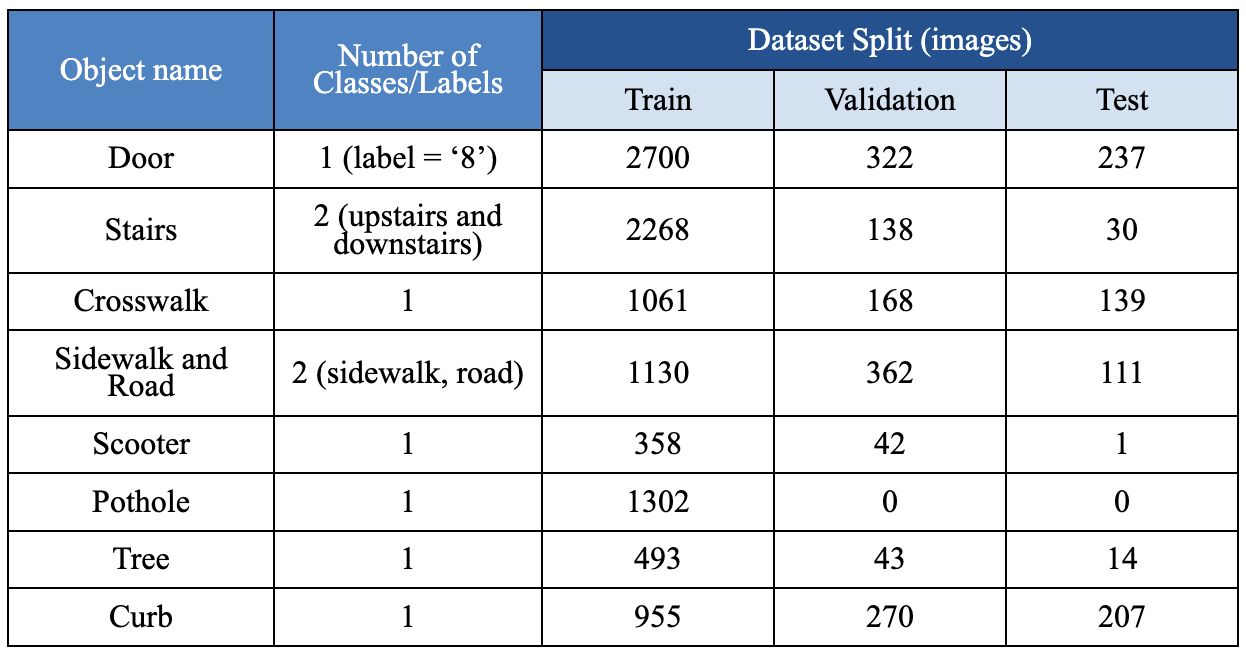
Dataset split showing training, validation, and test distributions across multiple object categories relevant to navigation scenarios.
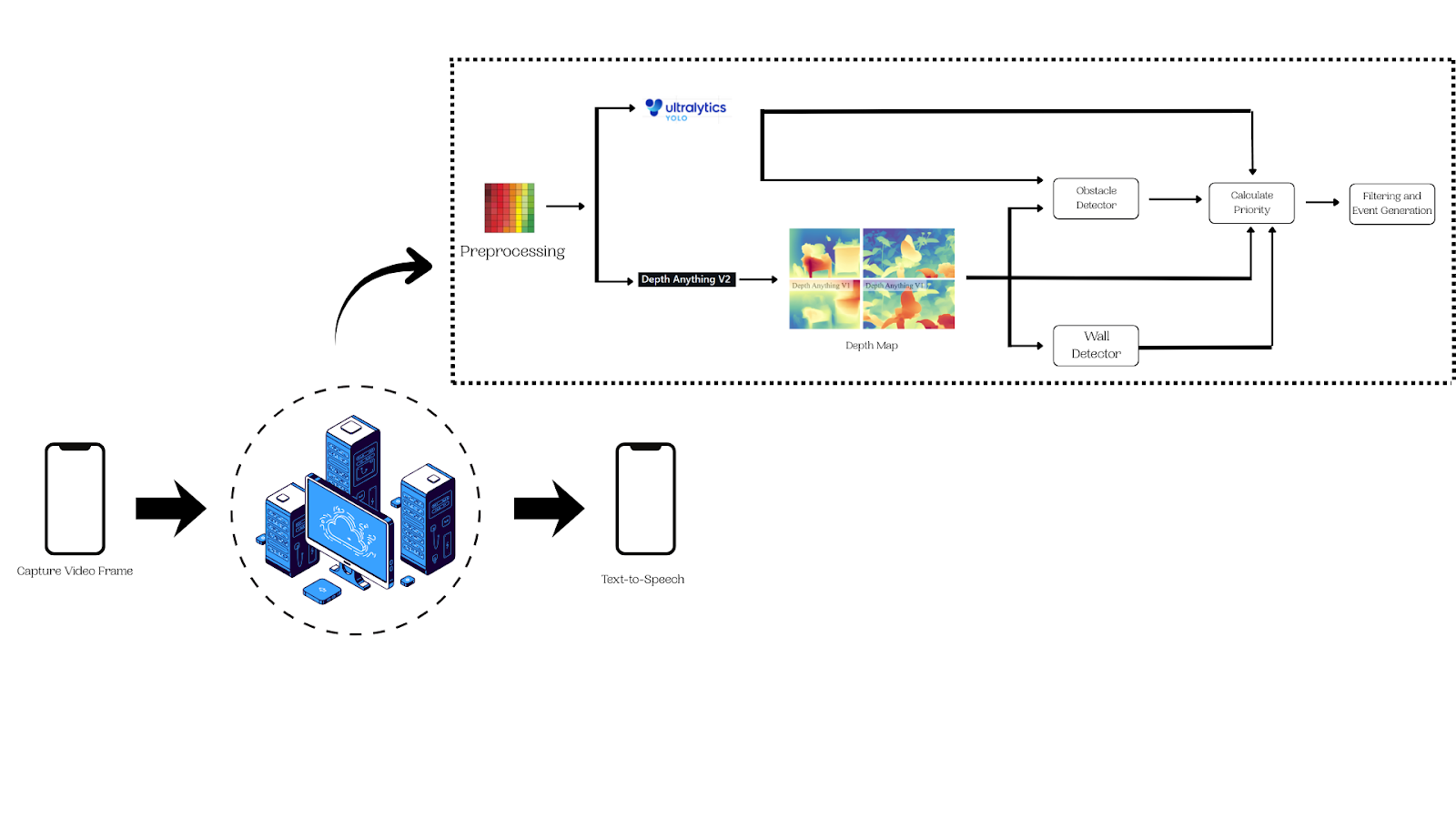
Smartphone captures live video and streams it to the backend via WebRTC. The video feed is continuously processed in real-time.
Each frame is processed by the following:
Depth data is matched to the detected objects to compute proximity, hazards, and direction information. Each detected object receives a hazard score based on its distance and type.
Only newly changed hazards pass through an anti-spam filter. Alerts are sent via WebSocket as JSON payloads and announced to the user via text-to-speech.
The custom-trained YOLOv11m model was evaluated on a dataset of 6,263 images containing 36,429 object instances. The model was fine-tuned to prioritize detection accuracy and generalization across diverse navigation scenarios.
| Metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Precision (Box P) | 0.766 |
| Recall (Box R) | 0.621 |
| mAP50 | 0.671 |
| mAP50-95 | 0.509 |
These metrics demonstrate strong detection accuracy with room for further optimization in recall and generalization across varying lighting and environmental conditions.
The Visual AI Companion successfully demonstrates the potential of combining computer vision and mobile technology to assist visually impaired individuals in navigating complex environments. By integrating real-time object detection, depth estimation, and text-to-speech feedback, the system provides actionable guidance that enhances independence and safety.
Future improvements include expanding the dataset for better generalization, optimizing model inference speed for lower-latency responses, and incorporating additional sensors (e.g., GPS, accelerometer) for enhanced contextual awareness.