- Pedestrian Detection
- Car Detection
- Image/Video Retargeting
- Computer Vision Applications on Embedded Multi-core Systems
- Over-segmentation Based Background Modelling and Foreground Detection
Pedestrian Detection
| Fri, 20 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
| Search Space Reduction in Pedestrian Detection for Driver Assistance System Based on Projective Geometry | |
| K. Dimza, T.F. Su, S.H. Lai. | |
| Vehicles are equipped with smarter and smarter driver assistance systems to improve driving safety year by year. On-board pedestrian detection system is a critical and challenging task for driving safety improvement because driving environment is very dynamic, where humans appear in wide varieties of clothing, illumination, size, speed and distance from the vehicle. Most of existing methods are based on the sliding window search methodology to localize humans in an image. The easiest and also the most popular way is to check the whole image at all possible scales. However, such methods usually produces large number of false positives and are computationally expensive because large number of inappropriate regions were checked. In this paper, we develop a method which reduce the search space in pedestrian detection by using properties of projective geometry in the case when camera parameters are unavailable. The simple user interaction with stochastic optimization is used to estimate projective parameters. We showed the efficiency of our method on public dataset with known camera parameters and self captured dataset without registered camera parameters. Experiment results show that the effectiveness of the proposed method is superior compared to the traditional uniform sliding window selection strategy. |
| Fri, 20 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
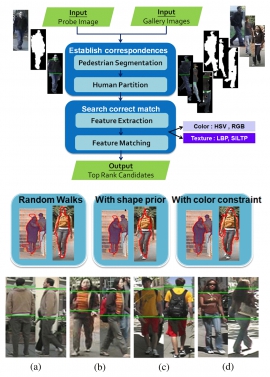
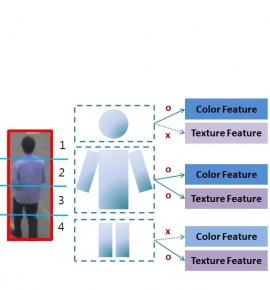
| Single-shot person re-identification based on improved Random-Walk pedestrian segmentation | |
| Y.-C. Chang, C.-K. Chiang and S.-H. Lai | |
| Single-shot person re-identification is to match pedestrian images captured from different cameras at different time under the condition of large illumination variations, different viewpoints, and inadequate information of single-shot case. To deal with these challenges, we propose a four-step single-shot person re-identification algorithm that consists of pedestrian segmentation, human region partitioning, feature extraction and human feature matching. Based on an improved Random Walks algorithm, human foreground is segmented by combining the shape prior information and the color seed constraint into the Random Walk formulation. Then color features of HSV histogram and 1-D RGB signal along with texture features from human body parts are used for the person re-identification. The correct match is then determined by the similarity scores of all features with appropriate weight selection. The experimental results demonstrate the superior performance by using the proposed algorithm compared to the previous representative methods. |
| Wed, 24 Nov 2010 - wowowo | |
| Video Surveillance from Pedestrian Detection | |
| 張幼臻, 王芳瑜, 李郁慈, 蘇德峰, 江振國 | |
| Pedestrian detection is helpful to video surveillance when the crime happens. To search a pedestrian from a recorded video database, the background model is built based on a mixture Gaussian model. This model is updated by successive frames to accommodate the lighting change. Then, moving objects are detected via background subtraction. Two classifiers, pixelwise classifier and region-based classifier, are used to remove noises and shadows of objects. After obtaining complete foreground objects, different features, like color, texture, are extracted from each body segment, head, torso and legs. Then, cross matching is performed to ensure effective feature matching. In addition, color consistency is also considered for extremely dark or bright clips. |
Car Detection
| Wed, 25 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
| Fast Vehicle Detector for Autonomous Driving | |
| Che-Tsung Lin, Patrisia Sherryl Santoso, Shu-Ping Chen, Hung-Jin Lin and Shang-Hong Lai | |
| This paper presents a fast vehicle detector which can be deployed on NVIDIA DrivePX2 under real-time constraints. The network predicts bounding boxes with different aspect ratio and scale priors from the specifically-designed prediction module given concatenated multi-scale feature map. A new data augmentation strategy is proposed to systematically generate a lot of vehicle training images whose appearance is randomly truncated so our detector could detect occluded vehicles better. Besides, we propose a non-region-based online hard example mining framework which performs fine-tuning by picking (1) hard examples and (2) detection results with insufficient IOU. Compared to other classical object detectors, this work achieves very competitive result in terms of average precision (AP) and computational speed. For the newly-defined vehicle class (car+bus) on VOC2007 test, our detector achieves 85.32 AP and runs at 48 FPS and 30 FPS on NVIDIA Titan X & GP106 (DrivePX2), respectively. |
| Tue, 24 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
| Integrated Vehicle and Lane Detection with Distance Estimation | |
| Yu-Chun Chen, Te-Feng Su, Shang-Hong Lai | |
| In this paper, we propose an integrated system that combines vehicle detection, lane detection, and vehicle distance estimation in a collaborative manner. Adaptive search windows for vehicles provide constraints on the width between lanes. By exploiting the constraints, the search space for lane detection can be efficiently reduced. We employ local patch constraints for lane detection to improve the reliability of lane detection. Moreover, it is challenging to estimate the vehicle distance from images/videos captured form monocular camera in real time. In our approach, we utilize lane marker with the associated 3D constraint to estimate the camera pose and the distances to frontal vehicles. Experimental results on real videos show that the proposed system is robust and accurate in terms of vehicle and lane detection and vehicle distance estimation. |
| Mon, 23 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
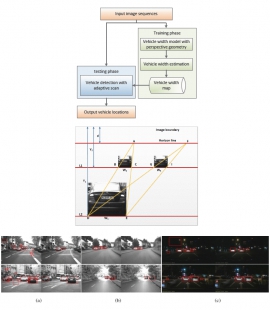
| Efficient vehicle detection with adaptive scan based on perspective geometry | |
| Yu-Chun Chen, Te-Feng Su, and Shang-Hong Lai | |
| Vehicle detection is an important research problem for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems to improve driving safety. Most existing methods are based on the sliding window search framework to locate vehicles in an image. However, such methods usually produce large numbers of false positives and are computationally intensive. In this paper, we propose an efficient vehicle detection algorithm that dramatically reduces the search space based on the perspective geometry of the road. In the training phase, we search a few images to locate all possible vehicle regions by using the standard HOG-based vehicle detector. Pairs of vehicle candidates that satisfy the projective geometry constraints are used to estimate the linear vehicle width model with respect to y coordinates in the image. Then an adaptive scan strategy based on the estimated vehicle width model is proposed to efficiently detect vehicles in an image. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm provides improved performance in terms of both speed and accuracy compared to standard sliding-windows search strategy. |
| Sun, 03 Feb 2013 - tfsu | |
| EFFICIENT VEHICLE DETECTION WITH ADAPTIVE SCAN BASED ON PERSPECTIVE GEOMETRY | |
| Yu-Chun Chen, Te-Feng Su, and Shang-Hong Lai | |
| Vehicle detection is an important research problem for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems to improve driving safety. Most existing methods are based on the sliding window search framework to locate vehicles in an image. However, such methods usually produce large numbers of false positives and are computationally intensive. In this paper, we propose an efficient vehicle detection algorithm that dramatically reduces the search space based on the perspective geometry of the road. In the training phase, we search a few images to locate all possible vehicle regions by using the standard HOG-based vehicle detector. Pairs of vehicle candidates that satisfy the projective geometry constraints are used to estimate the linear vehicle width model with respect to y coordinates in the image. Then an adaptive scan strategy based on the estimated vehicle width model is proposed to efficiently detect vehicles in an image. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm provides improved performance in terms of both speed and accuracy compared to standard sliding-windows search strategy. |
Image/Video Retargeting
| Tue, 23 Nov 2010 - Savan | |
| Image Compressibility Assessment and the Application of Structure-Preservng Image Retargeting | |
| Shu-Fan Wang and Shang-Hong Lai | |
| A number of algorithms have been proposed for intelligent image/video retargeting with important content retained as much as possible. In some cases, we can notice that they suffer from artifacts in the resized results, such as ridge or structure twist. In this paper, we suggest that the compressibility of an image should be estimated properly first by analyzing the image structure to determine the optimal scaling factors for the resizing algorithm. To cope with this problem, we propose a compressibility assessment scheme by combining the entropies of image gradient magnitude and orientation distributions. In order to further improve the result, we also present a structure-preserving media retargeting technique that preserves the content and image structure as best as possible. Since we focus on protecting the content structure, a block structure energy is introduced with a top-down strategy to constrain the image structure inside to scale uniformly in either x or y direction. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed compressibility assessment scheme provides better preservation of content and structure in the resized images/videos than those by the previous methods. |
| Tue, 23 Nov 2010 - Savan | |
| Image Compressibility Assessment and the Application of Structure-Preservng Image Retargeting | |
| Shu-Fan Wang and Shang-Hong Lai | |
Computer Vision Applications on Embedded Multi-core Systems
| Fri, 20 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
| Parallelized Background Substitution System on a Multi-core Embedded Platform | |
| Yutzu Lee, Chen-Kuo Chiang, Te-Feng Su, Yu-Wei Sun, Chi-Bang Kuan, Shang-Hong Lai | |
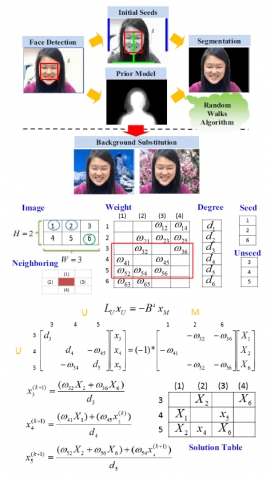
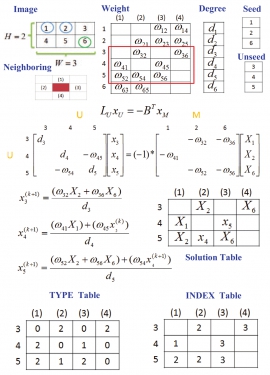
| We present an automatic human background substitution system based on a Random Walk (RW) algorithm on a multi-core processing architecture. Firstly, a fast algorithm is proposed to solve the large linear system in RW based on adapting the Gauss-Seidel method. Two tables, TYPE and INDEX, are introduced to fast locate the required data for the close-form solution. Then, face detection along with a human shape prior model are exploited to decide the approximated human body and background area. Pixels inside these areas are used as seed points in RW algorithm for automatic segmentation. The proposed method is designed to be highly parallelizable and suitable for running on a multi-core architecture. We demonstrate the parallelization strategies for the proposed fast RW algorithm and face detection on heterogeneous multi-core embedded platform to make the most use of the system architecture. Compared to the single processor implementation, the experimental results show significant speedup ratio of the parallelized human background substitution system on a multi-core embedded platform, which consists of an ARM processor and two DSP cores. |
| Fri, 20 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
| Parallelized Random Walk algorithm for background substitution on a multi-core embedded platform | |
| Y. Lee, C.-K. Chiang, Y.-W. Sun, T.-F. Su, S.-H. Lai | |
| Random Walk (RW) is a popular algorithm and can be applied to many applications in computer vision. In this paper, a fast algorithm is proposed to solve the large linear system in RW based on adapting the Gauss-Seidel method on a multi-core embedded system. Two tables, TYPE and INDEX, are introduced to fast locate the required data for the close-form solution. The computational overhead, along with the memory requirement, to solve the linear system can be reduced greatly, thus making the RW algorithm feasible to many applications on an embedded system. In addition, the proposed fast method is parallelized for a heterogeneous multi-core embedded platform to make the most use of the benefits of the system architecture. Experimental results show that the computational overhead can be significantly reduced by the proposed algorithm. |
| Thu, 19 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
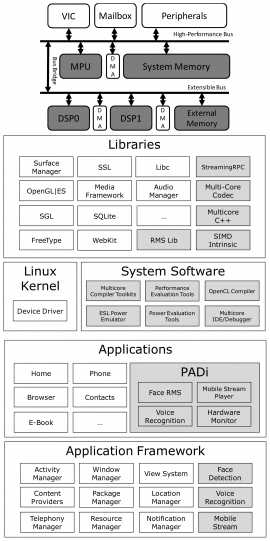
| Support of software framework for embedded multi-core systems with Android environments | |
| Y.-H.Chang, C.-B. Kuan, C.-Y. Lin, T.-F. Su, C.-T. Chen, J.-S. Jang | |
| Applications on mobile devices are getting more complicated with the new wave of applications in the mobile devices. The computing power for embedded devices are increased with such trends, and embedded multi-core platform are in a position to help boost system performance. Software frameworks integrated the multi-core platforms are often needed to help boost the system performance and reduce programming complexity. In this paper, we present a software framework based on Android and multi-core embedded systems. In the framework, we integrate the compiler toolkit chain for multi-core programming environment which includes DSP C/C++ compilers, streaming RPC programming model, debugger, ESL simulator, and power management models. We also develop software framework for face detection, voice recognition, and mobile streaming management. Those frameworks are designed as multi-core programs and are used to illustrate the design flow for applications on embedded multi-core environments equipped with Android systems. We demonstrate our proposed mechanisms by implementing two applications, Face RMS and voice recognition. The proposed framework gives a case study to illustrate software framework and design flow for emerging RMS-based and voice recognition applications on embedded multi-core systems equipped with Android systems. |
| Thu, 25 Nov 2010 - tfsu | |
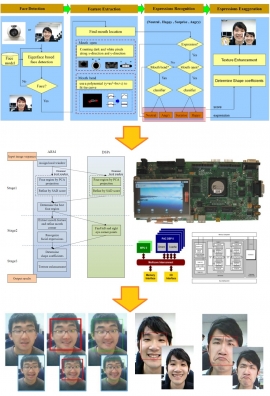
| Parallelized Face Based RMS System on a Multi-core Embedded Computing Platform | |
| 蘇德峰、曾聖博、段志學、王書凡、廖家德 | |
| The amount of data generated in the world continues to grow at an incredibly high speed. A new framework for the next generation, called the Recognition, Mining and Synthesis (RMS) system, was proposed to make meaningful use of the enormous amount of information on a multi-core processing architecture. Based on the same concept, we propose a face RMS system, which consists of face detection, facial expression recognition, and facial expression exaggeration components, for generating exaggerated views of different expressions on an input face image. In this paper, the parallel algorithms of the face RMS system were developed to reduce the execution time on a multi-core embedded system. The experimental results show the robustness of face detection with different scales and expressions in complex environments and an efficient non-linear method for expression exaggeration. The quantitative comparisons indicate the proposed parallelized face RMS system has a significant increase in speedup compared to the single processor implementation on the multi-core embedded platform, which consists of an ARM processor and two DSP cores. |
Over-segmentation Based Background Modelling and Foreground Detection
| Fri, 20 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
| From co-saliency to co-segmentation: an efficient and fully unsupervised energy minimization model | |
| K.-Y. Chang, T.-L. Liu, and S.-H. Lai | |
| Background subtraction is commonly used to detect foreground objects in video surveillance. Traditional background subtraction methods are usually based on the assumption that the background is stationary. However, they are not applicable to dynamic background, whose background images change over time. In this paper, we propose an adaptive Local-Patch Gaussian Mixture Model (LPGMM) as the dynamic background model for detecting moving objects from video with dynamic background. Then, the SVM classification is employed to discriminate between foreground objects and shadow regions. Finally, we show some experimental results on several video sequences to demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method. |
| Fri, 20 Jul 2018 - intern_james | |
| Detecting Moving Objects from Dynamic Background with Shadow Removal | |
| S.-C. Wang, T.-F. Su, and S.-H. Lai | |
| Background subtraction is commonly used to detect foreground objects in video surveillance. Traditional background subtraction methods are usually based on the assumption that the background is stationary. However, they are not applicable to dynamic background, whose background images change over time. In this paper, we propose an adaptive Local-Patch Gaussian Mixture Model (LPGMM) as the dynamic background model for detecting moving objects from video with dynamic background. Then, the SVM classification is employed to discriminate between foreground objects and shadow regions. Finally, we show some experimental results on several video sequences to demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method. |
| Thu, 25 Nov 2010 - tfsu | |
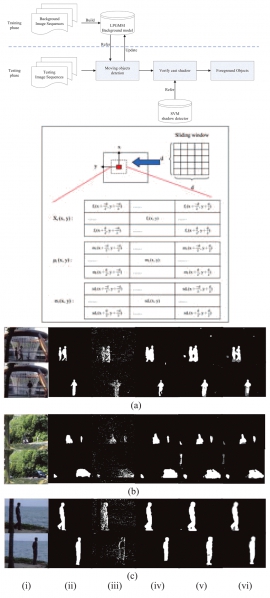
| Over-Segmentation Based Background Modeling and Foreground Detection with Shadow Removal by Using Hierarchical MRFs | |
| Te-Feng Su,Yi-Ling Chen and Shang-Hong Lai | |
| In this paper, we propose a novel over-segmentation based method for the detection of foreground objects from a surveillance video by integrating techniques of background modeling and Markov Random Fields classification. Firstly, we introduce a fast affinity propagation clustering algorithm to produce the over-segmentation of a reference image by taking into account color difference and spatial relationship between pixels. A background model is learned by using Gaussian Mixture Models with color features of the segments to represent the time-varying background scene. Next, each segment is treated as a node in a Markov Random Field and assigned a state of foreground, shadow and background, which is determined by using hierarchical belief propagation. The relationship between neighboring regions is also considered to ensure spatial coherence of segments. Finally, we demonstrate experimental results on several image sequences to show the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method. | |
| In Proceedings of Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV'10), Nov. 2010. | (pdf) |